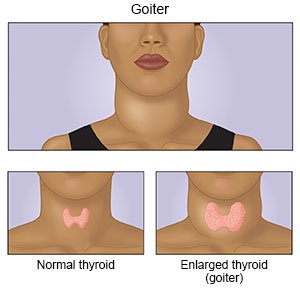
The thyroid gland is a tiny organ that requires a high concentration of iodine and selenium for proper functioning. The two elements have chemical affinity with thyroid hormones, so many environmental toxins can mimic their properties and damage the thyroid. The environment is full of heavy metals, including mercury, lead, and aluminum, which are all harmful to the body. Here are four specific heavy metals that can affect the function of the human Thyroid.
The most common industrial chemicals are dioxin, perchlorate, and perfluorinated chemicals. These chemicals are often used in manufacturing, as they are in high concentrations in the air and water. These substances impair thyroid function by imitating the structure of thyroid hormones and reducing the level of T4. These effects are seen at low levels of dioxin, and are therefore unavoidable.
Pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides are also known to impair thyroid function. The majority of people who have been exposed to pesticides and herbicides are affected by thyroid disease. These chemicals alter the thyroid hormone gene expression and prevent the uptake of iodine into the gland. They also decrease the absorption of thyroid hormone into the body. These pollutants have a negative effect on the brain and the nervous system, and are one of the leading causes of depression and obesity.
Toxins can affect your thyroid function, affecting your menstrual cycle, and your fertility. This disease is more common in women than in men, but symptoms do not include hair loss or skin problems. In addition to its negative effects, Thyroid disease can affect both men and women. Approximately one in every 100 women and one in every 1,000 men will have some level of thyroid disease at some point in their lives.
Thyroid disease affects millions of people around the world. The disease is a chronic, uncontrollable condition that can result in increased blood thyroid hormone levels. Thyroid diseases are often hereditary, and can run in families. If you have a family history of the disease, your doctor may suggest a course of treatment based on your symptoms and your family history. When diagnosed, Thyroid is toxic. can cause diarrhoea, hair loss, and depression.
Thyroid disease can affect your menstrual cycle, affect fertility, and cause hair loss. Thyroid diseases are more common in women than in men. Thyroid diseases can affect health at any age, but they are most common in women. It is important to get tested for symptoms as early as possible. Thyroid diseases often run in families and can be passed on from generation to generation.
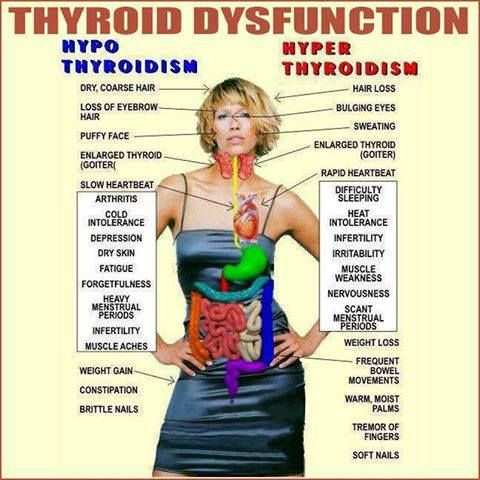
In rare cases, thyroid disease can affect your reproductive health. This may affect the length and quality of menstrual cycles. Some women may have irregular periods, while others may experience a decrease in sperm count. If you have already been diagnosed with a toxic thyroid gland, consult your doctor as soon as possible. This can cause heart problems, bone loss, and even compression of the windpipe. Although there are many causes of thyroid disease, it is best to consult a specialist to determine the best treatment options.
Thyroid disease can affect your reproductive health. This may cause irregular menstrual cycles. It can also affect fertility. If you have this disease, you may experience it at any age. Some women suffer from hair loss, itching and even hair loss. This condition can also affect the health of your skin, which can affect your quality of life. Despite the risk of developing thyroid disease, it is a relatively rare health problem.
Fortunately, the thyroid gland is not a rare disease. About one percent of the population in the United States has thyroid toxicity. It can be inherited or acquired. This is a genetic disorder that may be a symptom of another condition. Some people may not even know they have this condition. If you suspect you have thyroid toxicity, your doctor Mahendra Pratama
will offer you treatment options. Symptoms will depend on your age and the severity of the problem.
An overactive thyroid is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces excess amounts of thyroid hormones. An overactive thyroid gland can lead to a variety of health problems, including heart rhythm problems and osteoporosis. If left untreated, the thyroid gland is toxic. and can be treated with medications. For symptoms of thyroiditis, doctors can prescribe appropriate treatment. Thyroid medications can reduce the risk of thyroiditis and may be harmful.